The Bonaparte dynasty held many titles and territories during the Napoleonic war.
Markers required to participate in this project:
Y-DNA Markers
Y-DNA Haplogroup Tested
Y-DNA Subclade Tested
mtDNA Markers

Autosomal Markers

Y-DNA Markers
Y-DNA Haplogroup Tested
Y-DNA Subclade Tested
mtDNA Markers

Autosomal Markers

Profiles in this project


Determining the genetic profile of Napoleon
Napoleon was a military genius. His endeavors and personality dominated Europe during his time as Emperor. Unfortunately, his only legitimate son and heir, Napoleon II, died before having any children. But it’s said that Napoleon may have still left behind a genetic legacy through several illegitimate children. This is the DNA story of how researchers determined the DNA profile of one of the most celebrated and controversial leaders in human history.

The great military commander Napoleon
Napoleon I (Napoléon Bonaparte) was one of the greatest military commanders in history. After rising to power on May 18, 1804, he dominated European and global affairs for a decade.
He led his French army to victory in many Napoleonic Wars against various European coalitions, and established a large empire across much of Europe.
Then in October 1813, Napoleon lost to a large Allied force in the Battle of Leipzig. He was forced to abdicate after the Allies captured Paris, and was later exiled to Elba (an island near Rome). Napoleon managed to escape from his exile and regain power.
His second reign was short-lived before he lost to a strengthened Allied force in the Battle of Waterloo. This time, he was exiled to the remote island of Saint Helena in the South Atlantic, where he died several years later from possible poisoning.
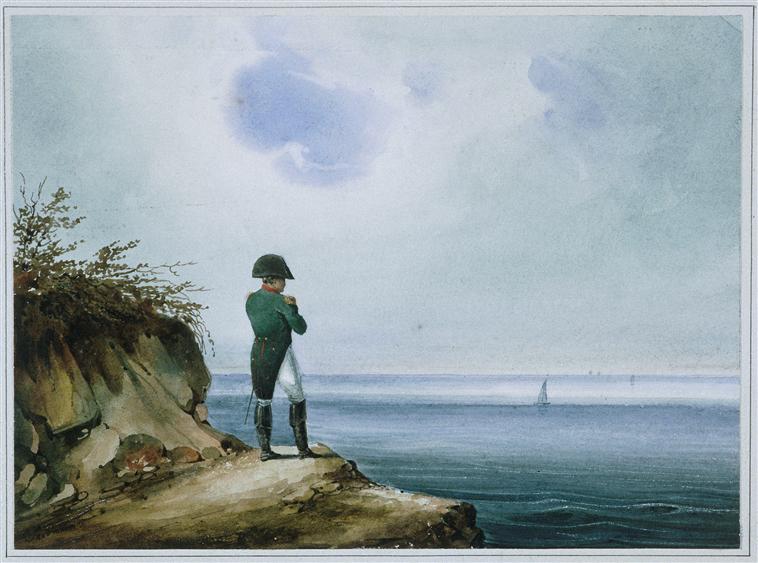

The genetic legacy of Napoleon
Napoleon’s first marriage took place when he was just 26 years old. Joséphine was the love of his life, but she failed to produce an heir.
Napoleon chose to divorce her, allowing him to remarry. He had one child, Napoleon II, with his second wife. Napoleon II was named as the new Emperor at just four years of age, when his father abdicated the throne.
However, the coalition partners that had defeated Napoleon refused to acknowledge his young son as his successor.
Napoleon II died in his early 20s without leaving any children. But that was not the end of Napoleon’s genetic legacy. Despite his lifelong love for Joséphine, Napoleon had multiple mistresses during both of his marriages.
He formally acknowledged one illegitimate son, Charles Léon. And it was widely known that he was also the father of Alexandre Colonna-Walewski. There are likely several other sons of Napoleon that spread his genes around Europe.
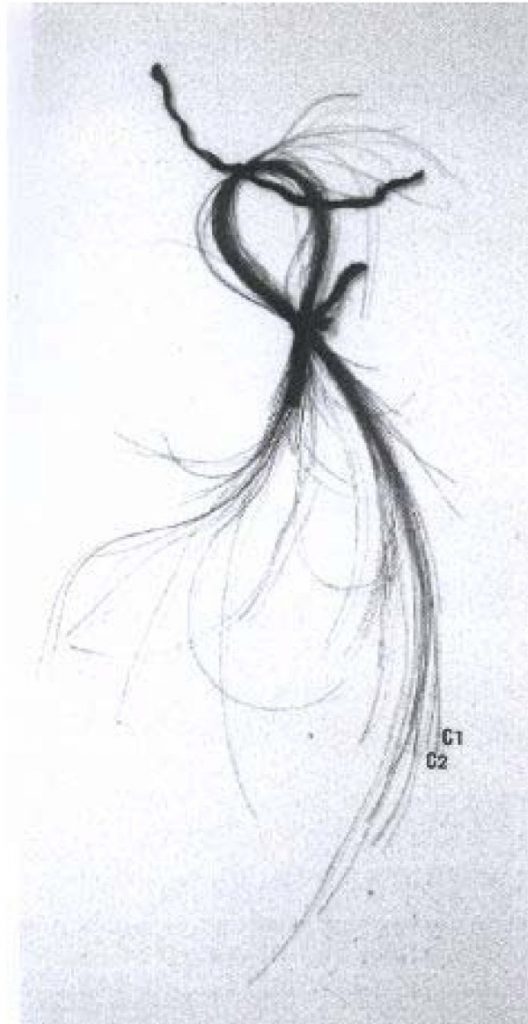


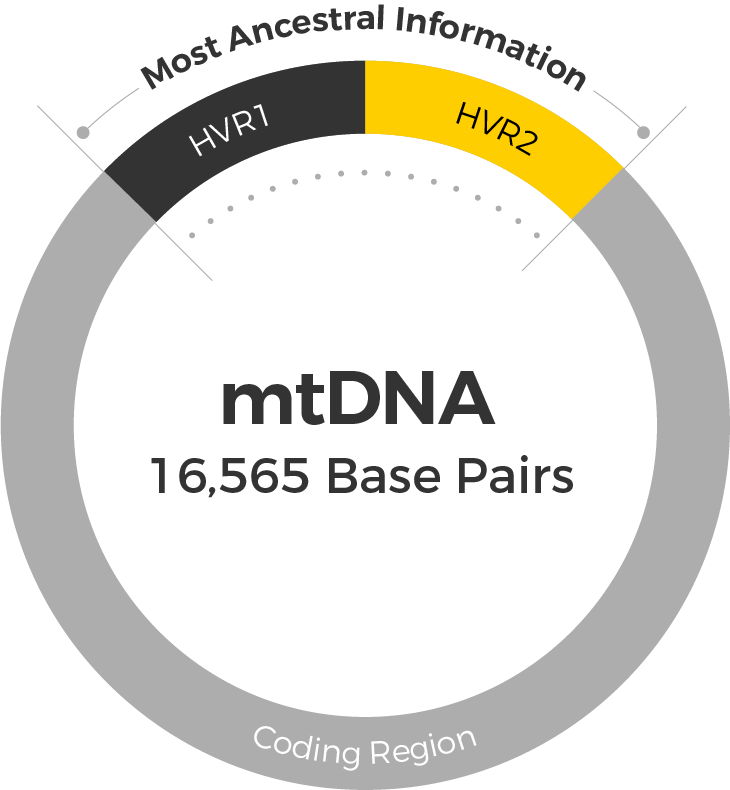
The mitochondrial DNA profile
How was Napoleon’s genetic profile determined? Believe it or not, researchers were able to obtain his DNA profile from a few strands of 200-year-old hair. These hairs were from the Vivant Denon reliquary – a late 15th (or early 16th) century reliquary filled with secular relics, including a signature, a fragment of a bloody shirt and a few strands of head and beard hairs, that are said to be from Napoleon.
But like many famous relics, there was always suspicion that the strands of hair may not have been authentic. To solve this problem, the researchers also analyzed the DNA from relatives of Napoleon.
The initial analyses focused on mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) – the only type of DNA that is strictly maternally inherited. Both males and females carry mtDNA, but only females pass it to the next generation. This means that a mother and all of her children share the exact same mtDNA profile. This profile stays virtually unchanged from generation to generation through the maternal line.
The mtDNA profile obtained from Napoleon’s presumed hair samples was a perfect match to hair samples from both his mother (Maria Letizia Ramolino) and his sister (Caroline, Queen of Naples). What’s more, this profile contains an extremely rare variant (16184C>T).
It has a frequency of less than 0.01% in the general population, meaning less than 1 in 10,000 people carry this sequence. The presence of this rare variant in all three of the samples, confirms that the hairs from the Vivant-Denon reliquary indeed belong to Napoleon.
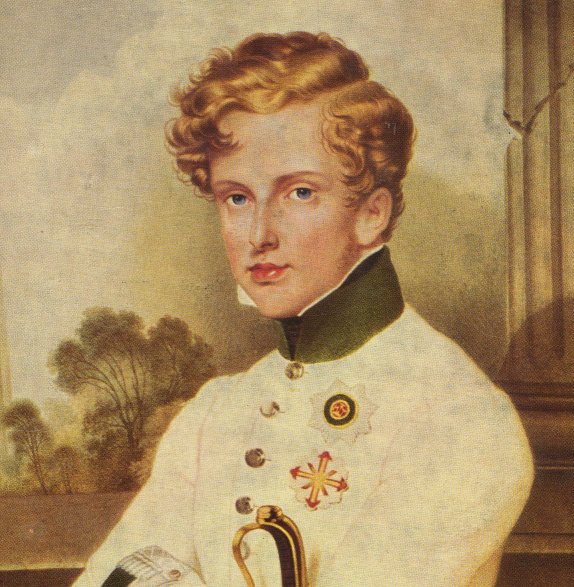

Tracing the paternal line
A second study used the hair samples to determine the Y-DNA profile of Napoleon. Y-DNA is passed down from father to son along the direct paternal lineage. Napoleon only had one legitimate son, who died before having any children, so there are no known paternal descendants of this great leader.
However, Napoleon shares the same Y-DNA profile as his biological brother, Jérôme (both inherited their Y-DNA from their father Carlo Buonaparte). All paternal descendants of Jérôme share this same Y-DNA profile.
So they can be used as references to confirm the Y-DNA profile obtained from the ancient hair sample. Fortunately for the researchers, Jérôme’s paternal great-great-grandson, Prince Charles Napoleon, agreed to provide DNA as a reference.
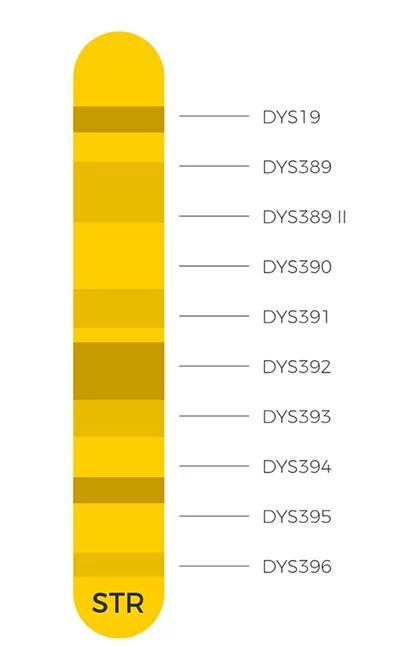
Y-DNA profiles
Two types of Y-DNA markers are available for analysis – very slow changing SNPs (single nucleotide polymorphisms) and fast changing STRs (short tandem repeats).
Researchers looked at ten SNP markers and three STR markers to uncover where Napoleon fitted in the Y-DNA evolutionary tree.
An evolutionary tree is like a family tree, showing all the different family groups. The major branches of the tree are called haplogroups identified by letters (A to T). Haplogroups can be thought of as ancient family groups that existed thousands of years ago.
Haplogroups are further divided into finer sub-branches known as subclades. Napoleon’s Y-DNA profile placed him in the E1b1b1c1* subclade. This was confirmed by identifying the same subclade for Prince Charles Napoleon.

Are you related to the first Emperor of the French?
Together these studies have defined both the mtDNA and Y-DNA profiles of Napoleon, one of the greatest commanders in history. The very rare mtDNA variant (16184C>T) is especially useful for identifying people who descended from the same maternal lineage as Napoleon.

It’s also an ideal tool for authenticating many other relics of Napoleon (body and hair samples) in collections worldwide. With Napoleon’s Y-DNA profile it’s possible to trace paternal descendants of the first Emperor of the French, and confirm the claim that he had many illegitimate children.
If you have taken the DNA Maternal Ancestry Test, you can compare your mtDNA against Napoleon’s mtDNA profile to see if you may have descended from the same maternal lineage.
Likewise, if you have taken the DNA Paternal Ancestry Test you can compare your Y-DNA against Napoleon’s Y-DNA STR markers to determine if you may have descended from the same paternal lineage as Napoleon Bonaparte.
